End-to-End Procurement in Highly Regulated Industries
December 11, 2025 | By Jabil Procurement & Supply Chain Team
Building Resilience, Compliance, and Agility Across Healthcare, Aerospace, and Automotive
Every industry breakthrough starts with a promise, to heal faster, fly farther, or move more efficiently. But delivering on that promise depends on thousands of coordinated decisions happening long before a product reaches the world. It’s in those decisions, what to source, who to trust, and how to sustain integrity, that procurement becomes the unsung force behind innovation and reliability.
Procurement today is not simply about securing materials or negotiating prices; it’s about ensuring that every product, part, and process meets the highest standards of quality, compliance, and sustainability. In sectors like healthcare, aerospace, and automotive, that responsibility carries greater weight. These industries operate under constant scrutiny, where a lapse in traceability, ethics, or resilience can have far-reaching consequences.
For leaders in these fields, end-to-end procurement has become the foundation of trust, linking engineering, manufacturing, and compliance in one intelligent, auditable ecosystem. Companies who can master modern procurement strategies are redefining how regulated industries compete and grow.

The Regulatory and Industry Landscape: A Converging Challenge
Innovation only scales when compliance, resilience, and supplier integrity are designed into procurement from the start. The following industry snapshots illustrate how these elements converge across healthcare, aerospace, and automotive to define modern operational excellence.
Healthcare and Medtech: Regulated Innovation
The healthcare sector continues to advance at the intersection of innovation and compliance. OEMs are racing to introduce smarter, more personalized devices while navigating evolving regulatory frameworks around AI in healthcare, data privacy, and cybersecurity.
AI-driven diagnostics, robotic-assisted surgery, and connected medical devices have become central to care delivery. These technologies generate immense volumes of sensitive patient data, which must be protected under laws such as HIPAA, the EU AI Act, and GDPR. Procurement teams play a frontline role in ensuring every supplier, from software developer to packaging manufacturer, meets stringent data and quality standards.

The industry’s supply chain model is also shifting. As outlined in Jabil’s 2025 Healthcare Market Intelligence Report, OEMs increasingly rely on specialized manufacturing partners to access advanced robotics, additive manufacturing, and vertical integration capabilities. Outsourcing has become a strategic partnership model enabling OEMs to expand capacity and accelerate time-to-market while maintaining compliance oversight.
Healthcare Procurement Strategies
Healthcare procurement strategies act as an innovation enabler and a compliance gatekeeper, embedding privacy, cybersecurity, and quality requirements into every sourcing decision. Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Bake compliance-by-design (privacy, cybersecurity, GMP/quality) into supplier onboarding, contracts, and continuous monitoring.
- Use digital twins and demand sensing to stress-test launches, inventory, and post-market surveillance obligations.
- Stand up decentralized procurement playbooks for home/virtual care (kitting, calibration, replacement flows, secure data handling).
- Partner with specialized manufacturers for advanced processes while maintaining auditable traceability and change control.
- Operationalize sustainability (materials, packaging, reverse logistics) with measurable supplier scorecards.
Aerospace and Defense: Compliance in Orbit
Few industries embody regulatory complexity more than aerospace and defense. Demand for secure satellite communications, in-flight connectivity, and IoT-enabled defense systems is accelerating the shift to software-defined satellites and modular platforms. These advances lower unit cost and speed iteration, but they also raise the bar on component pedigree, export control, and cyber assurance.
Capacity is a persistent constraint. As detailed in Jabil’s Satellite Communications Market Report, manufacturing for advanced HTS and LEO components remains tight, lead times are long, and specialized suppliers are few. That reality forces procurement to choreograph multi-tier suppliers with precision, ensuring every part, down to firmware and data handling, meets ITAR, DFARS, and other export-control standards while maintaining schedule integrity.

Regulatory oversight continues to intensify. Contractors are expected to attest to compliance beyond first-tier vendors, with significant penalties for false certifications under the False Claims Act. In parallel, modernization programs increasingly depend on AI and advanced analytics to predict failures, optimize maintenance, and strengthen mission readiness, requiring procurement to align engineering, cybersecurity, and legal in one auditable ecosystem.
A&D Procurement Strategies
Procurement is the control tower for integrity and speed, hardwiring compliance into design choices and supplier selection while keeping programs on schedule. Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Mandate end-to-end traceability (component pedigree, SBOMs, firmware versions, secure data transit) with continuous monitoring and evidence trails.
- Pre-qualify and audit suppliers, and sub-tiers, on export controls and cybersecurity; tie awards to verifiable controls and incident-response readiness.
- Align contracting with modular design (configuration control, change management) so updates move fast without jeopardizing certifications.
- Use scenario planning for long-lead items: capacity reservations, strategic buffers, and dual-sourcing where permitted.
- Enforce secure collaboration across the value chain (zero-trust access, encryption, role-based design data sharing) to protect CUI and program IP.
Automotive: Navigating Electrification and Policy Turbulence
Automotive manufacturing is shifting from metal to code, and procurement is feeling it first. As outlined in Jabil’s Automotive Market Intelligence Report, global vehicle sales are forecast around 89.79 million units, edging up from the prior year while trade volatility and shifting regulation continue to shape OEM strategy. Electrification remains central: BEV sales are projected at 14.9 million units, roughly 30% year-over-year growth and 16.6% share. Still, momentum is uneven, North America and parts of Europe face affordability and charging-infrastructure constraints that slow adoption curves.

Technology is redefining where value is created. Software-defined vehicles (SDVs), with centralized electronic architectures and over-the-air (OTA) updates, shift sourcing upstream to software, sensors, compute, and data governance. Cybersecurity, interoperability, and lifecycle patching are now core supplier qualifications. On the supply side, semiconductor and power-electronics dependencies demand long-horizon capacity planning and tighter OEM–Tier alliances; co-investment models are emerging to stabilize critical throughput.
Policy and sustainability add another layer. The EU Battery Regulation, CSDDD, and CBAM are accelerating localized production, low-carbon materials, circularity, and recycling thresholds. Evolving trade policies and shifting global alliances continue to underscore the need for trade-insulated cost models and region-by-region sourcing strategies. At the same time, transparency and traceability have become core procurement metrics as suppliers face increasing pressure to disclose emissions, energy use, and ethical sourcing practices.
Automotive Procurement Strategies
Procurement is the integrator of software, electronics, and sustainability, hardwiring resilience and compliance into a regionally balanced supply base. Here’s what that looks like in practice:
- Treat software & electronics as primary categories: require SBOMs, secure-by-design standards, OTA governance, and lifecycle patch/rollback plans.
- Build regional dual-sourcing and tariff scenarios into total cost: negotiate flexible capacity and price bands tied to policy triggers.
- Secure semiconductor/power-electronics with long-term agreements, buffer strategies, and selective co-investment where justified.
- Enforce battery-material traceability and recycling thresholds; align awards to verified low-carbon intensity and end-of-life plans.
- Operationalize circularity (recycled content, design for disassembly) with auditable supplier scorecards and chain-of-custody.
- Stand up data and cybersecurity controls across the supply base: mandate incident readiness, encryption, and conformity with connected-vehicle standards.
- Use predictive analytics for demand and constraint sensing, pre-plan alternates for critical components and logistics lanes.
Cross-Industry Procurement Trends
Healthcare, aerospace, and automotive build very different products, but their procurement realities are converging. Each must balance compliance with innovation and cost with resilience. Five trends are reshaping how leaders design end-to-end procurement.

1. Digital Twins & Predictive Analytics
Simulation is moving from pilot to core capability. Digital twins let teams test supplier performance, manufacturing yield, logistics constraints, and compliance scenarios before they commit capital.
- What’s changing: Many procurement executives now view digital twins as a core enabler of smarter, faster decision-making across complex supply chains. Instead of relying solely on historical data, they use real-time simulation to test production scenarios, predict supplier performance, and validate compliance before execution.
- Healthcare example: Digital twins are being used as virtual, data-connected models of patients, medical devices, and even entire hospitals to improve how care is delivered and managed. By mirroring real-world data in real time, they enable personalized treatment planning, remote patient monitoring, surgical rehearsal, and virtual clinical trials. The global healthcare digital-twin market is valued at roughly $903 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a 26% CAGR through 2030, with hospitals leading adoption.
- Why it matters to procurement: Digital twins not only accelerate PPAP/validation cycles but also help procurement teams pressure-test supplier capacity, forecast regulatory bottlenecks, and de-risk launch plans before parts, tooling, or production processes are finalized. As healthcare adoption grows, procurement must ensure data integrity, security, and compliance are embedded in every digital-twin ecosystem.
2. AI-Driven Procurement & Automation
AI is now embedded from sourcing to payment, flagging anomalies, modeling demand, and scanning supplier data for compliance risks.
- What’s changing: Organizations are accelerating their use of AI to manage growing supply chain complexity and operational risk. From sourcing and supplier evaluation to inventory management and quality control, AI is streamlining routine decisions, detecting anomalies in real time, and improving the precision of demand forecasting.
- Automotive example: AI is increasingly used to manage constrained categories like semiconductors and power electronics, helping automakers prioritize parts for the highest-impact programs. This shift aligns with new U.S. Department of Energy guidance under the 30D New Clean Vehicle Credit, which starting in 2025 makes vehicles ineligible for tax credits if their critical minerals come from a foreign entity of concern, pushing manufacturers to source materials locally.
- Why it matters to procurement: ML-based risk scoring and invoice automation reduce cycle time while improving first-pass compliance, particularly when aligned to regulatory screens (export controls, data-handling rules).
3. Resilience & Regionalization
Global efficiency alone is brittle. Leaders are shifting from “best-landed cost” to trade-insulated cost, explicitly modeling tariffs, policy risk, and logistics shocks.
- What’s changing: Supply chains are re-basing around regional hubs. Companies are redesigning networks so critical parts can be sourced and built in-region, with tariff-aware cost models, dual-qualified suppliers, and contingency routes. The goal: shorter lead times, less exposure to policy changes, and faster recovery when disruptions hit.
- Evidence of migration: Footprints are tilting toward North America, Europe, and “China+1” in Asia. Markets are seeing more localized battery and electronics capacity, multi-node manufacturing (one global design, several regional plants), and longer-term capacity reservations with key suppliers.
- Why it matters to procurement: Awards now prioritize resilience, not just price, favoring regional dual-sourcing (and second tooling), option clauses with index/tariff-linked pricing, and landed-cost simulations that include duties, FX, and freight. Teams are also pre-qualifying alternates and designing for interchangeability, holding buffer stock with live supplier-risk monitoring, and investing in traceability and circularity to keep supply compliant and flexible.
4. Sustainability as a Core Metric
Carbon, circularity, and provenance have moved from CSR to contract language.
- What’s changing: The EU Battery Regulation (2023/1542) imposes due-diligence, recycled-content, and digital passport requirements across the battery lifecycle; new Commission rules specify how recycling efficiency and recovery must be calculated and verified.
- Healthcare anchor: In pharma distribution, the DSCSA mandates interoperable, electronic, package-level traceability, tightening expectations for supplier data integrity and end-to-end tracking.
- Why it matters to procurement: Vendor scorecards now weight emissions intensity, recycled content, and traceability alongside cost and quality; awards increasingly require auditable evidence to maintain eligibility under EU and U.S. rules.
5. Cybersecurity & Data Integrity
Digital ecosystems widen the attack surface. A single weak supplier can cascade into downtime, safety risk, or compliance failures.
- What’s changing: ENISA’s latest threat-landscape report finds supply-chain attacks account for up to 10.6% of observed threat activity, with OT threats 18.2%, underscoring rising risk to industrial systems as IT/OT converge.
- Real-world pressure: In 2025, third-party/supply-chain compromise accounted for 15% of breaches, carried an average cost of $4.91M, and had the longest lifecycle (267 days to identify + contain) among initial attack vectors.
- Why it matters to procurement: Supplier networks are now a primary cybersecurity risk, making protection a core procurement responsibility. Teams are requiring SBOMs, zero-trust data access, and verified patch management as standard terms to safeguard operations and stay eligible for defense, healthcare, and automotive contracts.
Building an End-to-End Procurement Framework
Managing regulatory complexity and technological change requires a system that connects strategy, compliance, and execution in real time. The following building blocks outline how leaders can evolve procurement into a resilient, intelligence-driven function built for regulated industries.
1. Governance and Alignment
Every transformation starts with governance. Build cross-functional structures that bring together procurement, legal, compliance, finance, and sustainability under shared accountability. Clearly define ownership for regulatory, ethical, and cybersecurity risks so that decision-making is consistent, traceable, and auditable across the enterprise.
2. Data Centralization and AI Integration
Data is the foundation of modern procurement. Consolidate fragmented systems into a unified source-to-pay (S2P) environment, ensuring data is accurate, accessible, and actionable. This creates the foundation for AI-driven analytics, unlocking predictive compliance checks, real-time spend visibility, and automated supplier scoring that turns information into intelligence.
3. Supplier Segmentation and Collaboration
True resilience depends on knowing which relationships matter most. Segment suppliers by criticality, regulatory exposure, and innovation potential. Develop strategic partnerships with those driving advanced manufacturing, sustainability, or R&D breakthroughs. Shared digital platforms and transparent data exchange strengthen trust and enable joint problem-solving when disruptions occur.
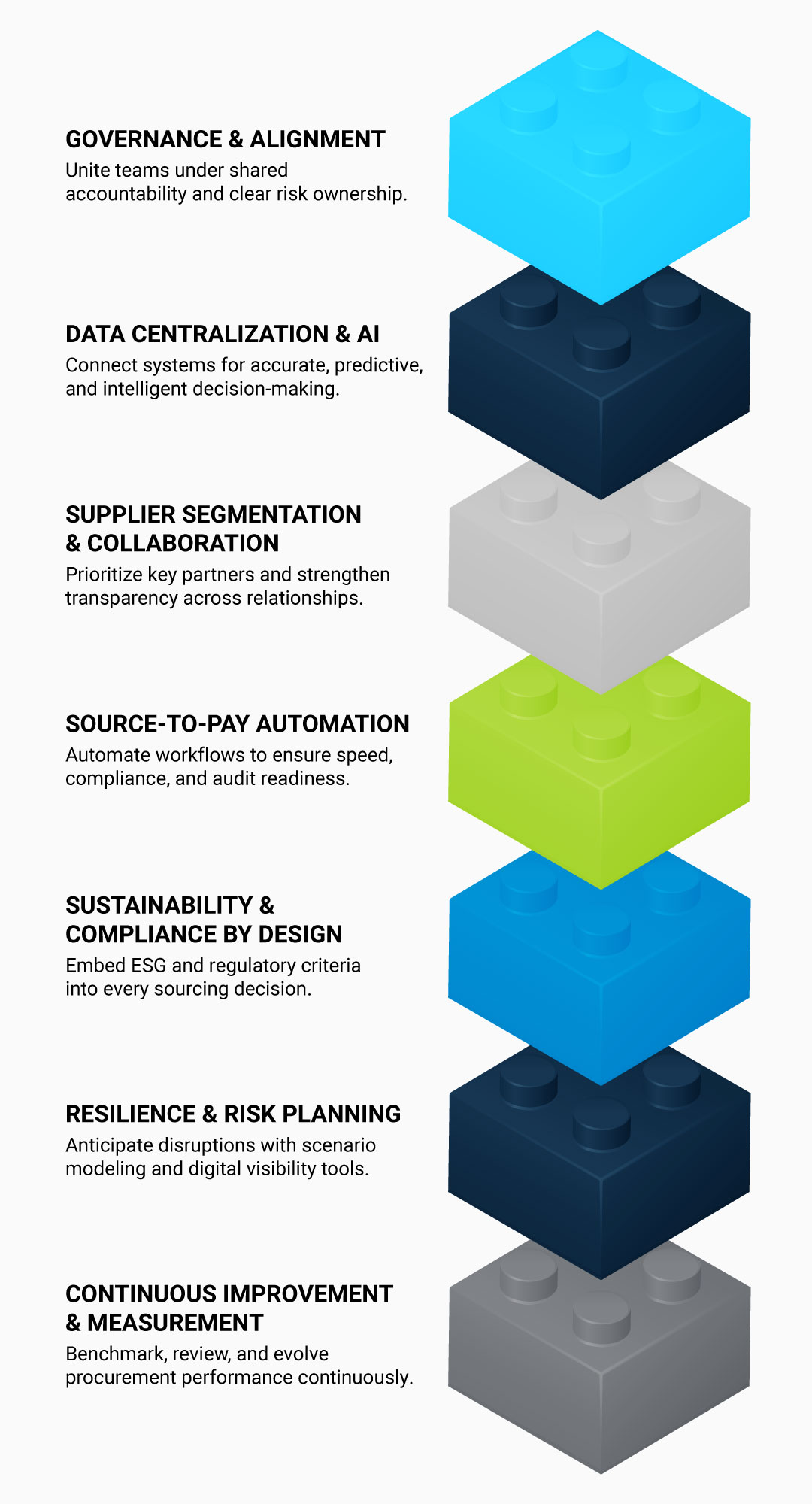
4. Integrated Source-to-Pay Automation
Automation is the bridge between strategy and execution. Modern S2P platforms, enhanced by AI, workflow automation, and blockchain, create a continuous digital thread from sourcing to payment. This eliminates manual bottlenecks, embeds compliance checks directly into each transaction, and ensures faster, error-free approvals that meet both audit and performance standards.
5. Sustainability and Compliance by Design
Sustainability and compliance are no longer parallel goals, they’re integrated design principles. Embed ESG and regulatory criteria directly into sourcing decisions using digital audits, automated scorecards, and traceability dashboards. From DSCSA in healthcare to ITAR/DFARS in aerospace and CSDDD in automotive, proactive compliance safeguards reputation and accelerates time to market.
6. Resilience and Risk Planning
Procurement must now anticipate disruption rather than react to it. Develop scenario models that account for tariff shifts, supplier outages, and material shortages. Multi-tier visibility tools and digital twins can map dependencies, simulate risk, and test contingency plans, giving leaders the foresight to re-source quickly and protect continuity.
7. Continuous Improvement and Performance Measurement
Procurement transformation never ends. Tie performance to business outcomes such as innovation speed, cost efficiency, risk reduction, and ESG progress. Use regular reviews, peer benchmarking, and supplier feedback loops to measure what works and where to adapt. The most successful teams treat every sourcing cycle as an opportunity to learn, refine, and lead.
The Future of Procurement in Regulated Industries
Procurement’s future lies in intelligence, not administration. As industries grow more connected and regulated, procurement will serve as the bridge between compliance and innovation, where data, technology, and supplier collaboration converge to create real strategic advantage.
Tomorrow’s leaders won’t just react to regulation or disruption; they’ll anticipate it. By integrating AI, automation, and predictive insight into sourcing and supplier management, organizations can turn complexity into clarity and resilience into growth.

Partnering with Jabil PSCS
Jabil Procurement & Supply Chain Services helps organizations design procurement ecosystems built for precision and compliance. From healthcare to aerospace to automotive, we combine digital visibility with hands-on expertise to help companies move faster, adapt sooner, and lead with confidence.